OVERVIEW
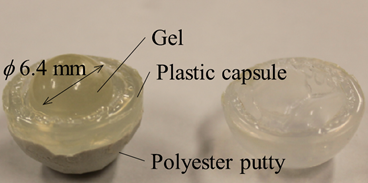
Several studies have investigated the combustion characteristics of gelled liquid fuels with the aim of increasing the energy density and improving the transport and storage safety. Ethanol based gelled fuels have been studied to control auto ignition or ignition delay.
poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPPAm) gel used as a polymeric gel storage for liquid fuels. Chemical gels are synthesized by polymerization in the presence of a cross-linking agent, and the networks of the chemical gels are chemically cross-linked.
MECHANISM
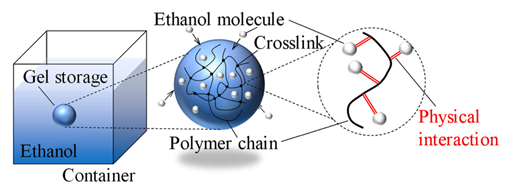
The polymeric gel storage includes innumerable three dimensional polymer chains that are cross-linked chemically. The ethanol molecules swell the polymeric gel storage and the polymer chains bond the ethanol molecules by physical interactions (ionic bond, hydrophobic interaction, etc.).
To disbond the ethanol from the polymer chains, it needs to add thermodynamic energy to the polymeric gel storage. Pure ethanol can extract from the polymeric gel storage by applying thermodynamic energy.
EVAPORATION CHARACTERISTICS

The evaporation area of the polymeric gel storage decreases as the evaporating time increases. The evaporation rate of the polymeric gel storage is extremely small.
The evaporating area of the polymeric gel storage changes during evaporating. If the size of the polymeric gel storage is larger, the trend of the evaporation rate of the polymeric gel storage may stay about the same.
COMBUSTION CHARACTERISTICS
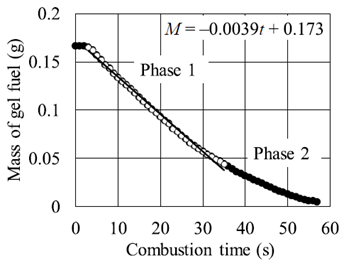
As the diameter of the polymeric gel storage increases, the burning rate constant increases. The polymeric gel storage is not consumed perfectly by combustion.
The mass of the burned embers increases as the initial diameter of the polymeric gel storage increases. If the higher combustion efficiency is needed, smaller diameter could be used.
Source : Hosoya, N., Nishiguchi, K., Saito, H., & Maeda, S. (2022). Chemically cross-linked gel storage for fuel to realize evaporation suppression. Chemical Engineering Journal, 136506.

No Responses