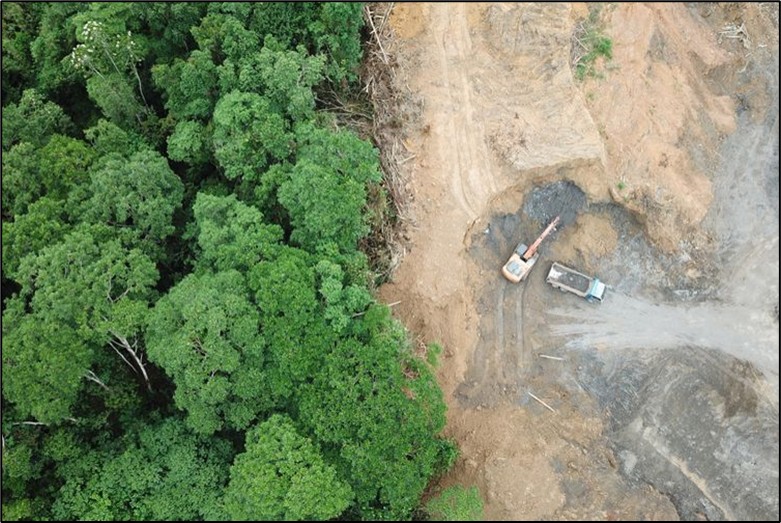

Illustration of deforestation, where rainforests in Kalimantan are cleared to make way for oil palm plantations.
Indonesian forests are often eferred to be the world's lungs because they provide oxygen for the survival of living things by absorbing toxic carbon dioxide and producing oxygen gas. Forests are natural resources that play a critical role in the economy, social, cultural, and environmental aspects of existence. The loss of forest land undoubtedly leads to the extinction of numerous species, which has a variety of consequences, including the greenhouse gas effect. The main environmental issues that developed were divided into five categories, for example, land damage etc, caused by logging and the conversion of land for plantations.
Land conversion to oil palm plantations accounts for 57 percent of deforestation in Indonesia, with pulp and paper accounting for another 20%. (Ariana, 2017). Almost every year, Indonesia is hit by devastating forest fires; in 2015, 1.7 million hectares burned, resulting in a haze disaster that had major consequences for education, air travel, health, the economy, and, of course, the environment.
Deforestation refers to the loss of forest land owing to land use agreements for infrastructure, settlements, agriculture, mining, and plantations (Addinul Yakin, 2017). As a result of the frequent forest fires, the conversion of forest land to non-forest land contributes to global warming. Deforestation is linked to illegal logging that poses a harm to all living things and is commonly triggered by forest fires that contribute to global warming (Rimbakita, 2020).
According to Greenpeace, Indonesia is the third-largest contributor to carbon dioxide emissions behind the United States and China, with forest burning accounting for about 80% of the total. Forest burning also has a significant influence on human health, producing shortness of breath (Han, Goleman, Boyatzis, & Mckee, 2019).
Official data from the Ministry of Environment and Forestry in recent years shows that it has declined by 75%, or 115.5 thousand hectares, in 2019-2020 compared to the 2018-2019 period, when it reached 462.5 thousand hectares. The high pace of deforestation each year will result in a large loss of forest land, posing a threat to the environment and social life, as well as having direct and indirect consequences in the future. Because the pace of forest deforestation might fluctuate year to year due to various human or community activities, cooperation and mutual knowledge are required to prevent forest deforestation and have a good impact on the environment and human health.
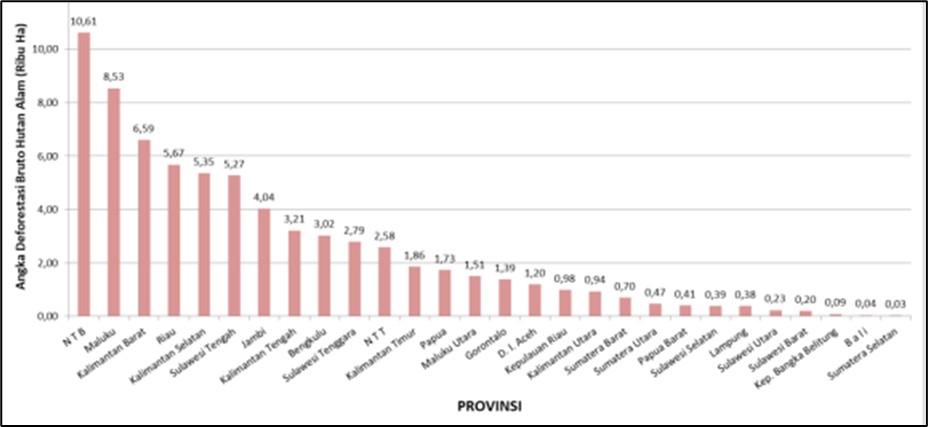
West Nusa Tenggara Province had the greatest Gross Deforestation Rate of Natural Forests, at 10.6 thousand ha (9.1%), followed by Maluku at 8.5 thousand ha (7.3%), West Kalimantan at 6.7 thousand ha (5.6%), Riau at 5.7 thousand ha (4.8%), and South Kalimantan at 5.4 thousand ha (5.4%). (4.6 percent).
Various factors that cause deforestation, namely:
- Farm conversion
- Forest fires
- Wood harvesting
Various actions that produce deforestation will have a significant negative influence on the quality of life, which will be felt immediately by all living beings. So that reductions can be made that will allow Indonesia's natural environment to be preserved with minimal effort.
The Impact of Deforestation on Global Warming.
Forest area has diminished due to land usage for infrastructure, communities, agriculture, mining, and plantations, posing a hazard to living creatures (Yakin, 2015). Deforestation in Indonesia has a significant national and international impact, as well as the presence of uncontrolled forest fires, clearing land for plantations, dredging fuel, and the development of transmigration areas. All of them have several impacts on the community and can result in significant losses, particularly for the entire society and country.
High emissions can cause various serious impacts including:
- Temperatures have increased since 1990 by about 0.3 Degree Celsius throughout the season.
- An increase of 2 to 3% of rainfall intensity every year
- Significantly increased risk of flood disaster.
- Creating food threats from the consequences of extreme climate change.
The image below shows how deforestation has changed the structure of forest distribution.
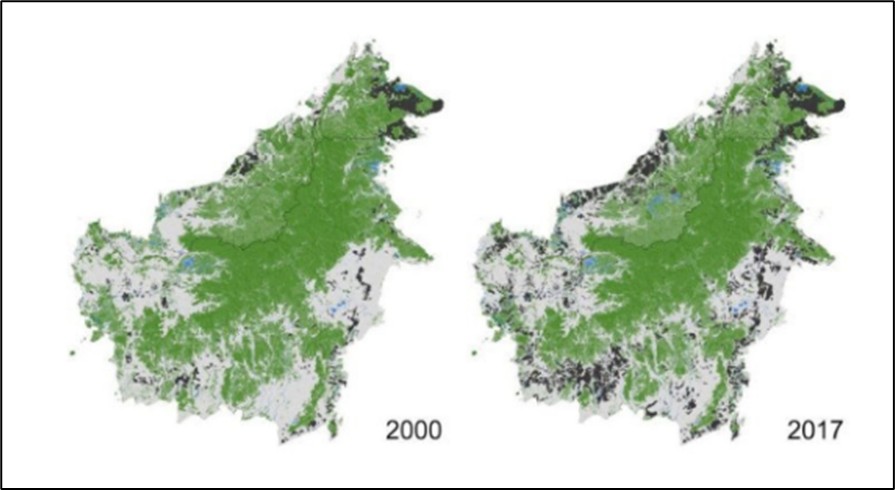
Changes in the Distribution of Forests Due to Deforestation
The island of Borneo gives statistics on forest land loss every year through 2020, based on the land map above, which is caused by land used for oil palm plantations and pulp wood plantations, which are highlighted in black on the map above. The change in colour from green to white shows the loss of forest land due to logging and conversion in the same year, whereas the green hue indicates that the forest is permanently dammed.
In Kalimantan, Indonesia has lost 73 percent of its land area, totalling 3.74 million hectares. 2.29 million hectares of forest land were lost on the island of Kalimantan, with 1.85 million hectares being utilised for plantations.
Deforestation Reduction Efforts
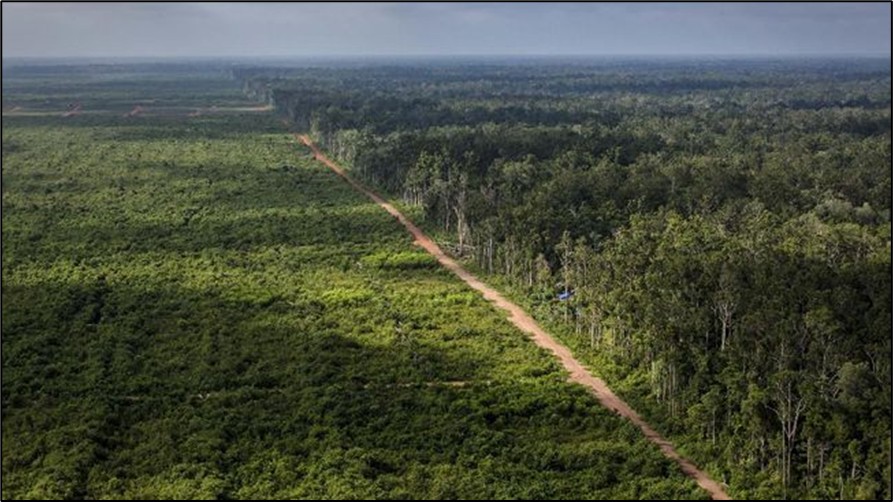

Indonesia succeeded in reducing deforestation by 75.03% in the 2019-2020 period, to 115.46 thousand ha. This data was released by the Directorate General of PKTL, KLHK.
Deforestation can be slowed down such that the rate of deforestation does not increase using a number of methods. Including selective logging system that can maintain the sustainability of forest ecosystems and function as a life support system. Then the reforestation initiatives, such as replanting in forest areas, might be used.
The 2020-2024 RPJMN includes a number of methods for mitigating forest deforestation, including replanting to decrease deforestation to 310 hectares per year.
CONCLUSION
Deforestation is a type of forest land loss that poses a harm to living things. Forest area has reduced because of land agreements for infrastructure, towns, agriculture, mining, and plantations, all of which have major consequences, including contributing to global warming. High emissions can have major consequences, such as temperature rises and increasing annual rainfall intensity, both of which can lead to disasters. The main element in deforestation by burning trees to shorten land clearing is the human component for clearing agricultural land and plantations in forest areas. Forest areas will eventually be converted as oil palm plantations expand. As a result, land degradation (land deterioration) will occur in areas where land productivity has declined. Burning land will also result in an increase in carbon emissions, which will have an impact on greenhouse gas emissions in the atmosphere. As a result, the sun's heat is trapped in the earth, resulting in global warming. If this continues, it will result in climate change.

Comments (0)